Welcome
This web server provides online access to a series of tools developed by the Freiburg Bioinformatics Group. To start using it, please select from the listings below, or use the menu on the left. If you prefer doing a local installation on your machine, please visit our 'Download' section.
If you use our tools for research or education, please cite the corresponding articles from the 'Publications' section.
Version 5.0.12
Freiburg RNA Tools
Freiburg RNA tools provides
online access to a series of RNA research tools developed by the
Freiburg Bioinformatics Group and colleagues for
sequence-structure alignments (LocARNA, CARNA, MARNA),
clustering (ExpaRNA),
interaction prediction (IntaRNA, CopraRNA, metaMIR),
identification of homologs (GLASSgo),
sequence design (AntaRNA, INFORNA, SECISDesign),
CRISPR repeat analyses (CRISPRmap),
and many more tasks.

Interaction Prediction
CopraRNA is a tool for sRNA target prediction. It computes whole genome
predictions by combination of whole genome IntaRNA
predictions using homologous sRNA sequences from distinct organisms.
IntaRNA enables the prediction of RNA-RNA interactions. It has
been designed to predict mRNA target sites for given non-coding RNAs
(ncRNAs) like eukaryotic microRNAs (miRNAs) or bacterial small RNAs
(sRNAs), but it can also be used to predict other types of RNA-RNA
interactions.
GLASSgo (GLobal Automated sRNA Search go) combines iterative BLAST
searches, pairwise identity filtering, and structure based
clustering in an automated prediction pipeline to find sRNA
homologs from scratch. The web server provides
predefined parameter sets for a non-expert usage
as well as enables a manual setup of the query parameters.
metaMIR is a microRNA (miRNA) framework to predict
interactions in human between miRNAs and clusters of genes. The user
provides a set of genes to be targeted, and optionally genes not to
be targeted. Taking data from a reference database of previously
established predictive algorithms, metaMIR will return miRNA
candidates predicted to co-regulate genes among those entered by
analyzing all possible subset combinations.
Seq-Str Alignment
LocARNA computes multiple alignments of RNAs based on their sequence and
structure similarity. In contrast to, e.g. MARNA, it considers the whole
ensemble of secondary structures for each RNA. Thus, LocARNA aligns RNAs
with unknown structure and predicts a consensus secondary structure for
a set of unaligned RNAs. Specification of additional
constraints or even enforcement of fixed input structures is possible.
LocARNA is best suited to compare structural RNAs, in particular, of low sequence similarity.
Carna is a tool for multiple alignment of RNA molecules based on their full
ensembles of structures. Carna computes the alignment that fits best to all likely structures
simultaneously. Hence, Carna is in particular useful to align RNAs
with more than one stable structure, as for example riboswitches,
and is able to align arbitrary pseudoknots.
MARNA computes multiple sequence-structure alignments considering
a single fixed structure for each sequence only.
ExpaRNA is a fast, motif-based comparison and alignment tool for RNA molecules.
Instead of computing a full sequence-structure alignment, it computes the best
arrangement of sequence-structure motifs common to two RNAs.
CRISPR
CRISPRmap provides a quick and detailed
insight into repeat conservation and diversity of both bacterial
and archaeal systems. It comprises the largest dataset of CRISPRs
to date and enables comprehensive independent clustering analyses
to determine conserved sequence families, potential structure
motifs for endoribonucleases, and evolutionary relationships.
CRISPRloci provides an automated and comprehensive in silico characteriztion
of CRISPR-Cas system on bacterial and archaeal genomes. It is a full suite for CRISPR
locus characteriztion that includes CRISPR array orientation, detection of conserved leaders,
cas gene annotation and subtype classification.
Sequence Design
AntaRNA is an Ant-Colony Optimization based tool which solves the RNA inverse
folding problem. It designs RNA sequences which satisfy a set of
constraints made by the user. The realized multi-objective optimization allows
to introduce structure, sequence and GC-content constraints.
INFO-RNA is a server for the design of RNA sequences that fold into
a given pseudo-knot free RNA secondary structure.
SECISDesign is a server for the design of SECIS-elements within the coding sequence of an
mRNA with both structure and sequence constraints. Furthermore, a certain similarity to the
original protein is kept. It can be used e.g. for recombinant expression of selenoproteins in E. coli.
Splicing
NIPU allows to display splicing regulatory motifs and single-stranded regions.
SNP & Mutation
CopomuS rates and ranks possible compensatory mutations of IntaRNA predictions
to support the design of verification experiments for putative RNA-RNA interactions.
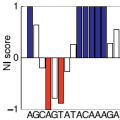
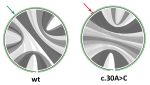
MutaRNA (Mutational Analysis of RNAs) predicts and visualizes the mutation-induced
structure changes of a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in an RNA sequence.
This covers changes in the accessibility (single-strandedness) of the molecule,
its intra-molecular base pairing potential and its the base pairing probabilities.
Combined with evaluation results of tools like remuRNA and RNAsnp,
MutaRNA enables a detailed evaluation of a mutation's effects on RNA structure formation.
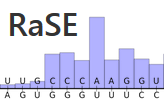
(offline) RaSE uses the graph vectorization technique of EDeN to
compute a score indicative of the structural stability responsibility
of each nucleotide in an RNA sequence. The score is computed as the
similarity of the structure obtained by changing a single nucleotide
with respect to the original structure. The structure is based on
RNAplfold base pair probabilities and thus reflects the overall
structural ensemble accessible to the RNA molecule.
Per sequence position, only the mutation which yields the largest
structural difference is reported.
Classification
BrainDead learns a two-class model for short RNA
sequences based on accessibility-enhanced k-mer features and applies
it for class prediction of unknown RNAs.
Gene set extension
Given a list of genes known to be associated with a given genetic disease,
DiGI predicts and ranks a list of unknown genes based on their probabilities
to be related to that disease.
The Freiburg Bioinformatics Group also provides:
MoDPepInt Server
MoDPepInt (Modular Domain Peptide Interaction)
is a simple and interactive webserver, which
comprises three different tools, i.e. SH2PepInt, SH3PepInt and PDZPepInt,
for predicting the binding partners of three
different modular protein domains,
i.e. SH2, SH3 and PDZ domains, respectively.
CPSP-Tools Server
CPSP (Constraint-based Protein Structure Prediction)
is an exact and efficient approach to identify optimal structures
of lattice proteins within the hydrophobic-polar (HP) model. The
approach enables structure prediction within the 3D cubic and
3D face-centered-cubic (FCC) lattice for both backbone-only as well
as side-chain representing models.
Galaxy Project - Uni Freiburg
The Freiburg Galaxy Team offers a framework for scientists on
e.g. NGS data analyses (RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, Exome-seq, MethylC-seq),
genome annotation analyses for eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms
(from gene prediction to functional description), Proteomics and
Metabolomics analysis, and the ChemicalToolBoX for analysis of
small compounds. Galaxy contains more than 800 different single
analysis tools and ready-to-use pipelines for different applications.
The Freiburg Galaxy Project is part of the “German Network for Bioinformatics Infrastructure” (Deutsches Netzwerk für Bioinformatik-Infrastruktur, de.NBI) and the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) 992 for Medical Epigenetics and offers within the RNA Bioinformatic Centre (RBC) a central platform for RNA analysis.
The Freiburg Galaxy Project is part of the “German Network for Bioinformatics Infrastructure” (Deutsches Netzwerk für Bioinformatik-Infrastruktur, de.NBI) and the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) 992 for Medical Epigenetics and offers within the RNA Bioinformatic Centre (RBC) a central platform for RNA analysis.